The How, What, When- Everything you Should Know about Ovulation
 53100
53100

super easy
What is Ovulation? If you remember your 8th-grade Biology classes, you will remember that Ovulation is described as the release of an egg during menstruation in females. The released egg travels down the fallopian tube, where it has a chance to be fertilized if sperms are present in the fallopian tube. Once a sperm fertilizes the egg, an embryo gets formed, and a woman is then pregnant. Estrogen and progesterone (female hormones) get released by the ovaries, and these hormones help with the building of a lining of the womb or uterus called the endometrium. This lining is necessary for the embryo to attach itself to the uterus and grow into a fetus (baby). The lining ruptures and bleeds if there is no embryo formed, and this exits via the female genitals (vagina) as menstrual blood.
Fertility and Ovulation
A section of the brain termed as hypothalamus controls the hormonal release and Ovulation during the menstrual cycle. The hypothalamus directs signals that instruct the pituitary gland and anterior lobe to secrete the Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and the Luteinizing Hormone (LH). These hormones are also termed gonadotropins as they stimulate the gonads – the testes in males and the ovaries in females. After menopause, these hormones play no role.
Women are most fertile during their ovulation time (when an egg gets released from the ovaries); this usually occurs around twelve to fourteen days before the next period starts. The ovulation time is that time of the month when a woman is most likely to get pregnant; it is not expected for a woman to get pregnant right after her periods (menses), although it is still a possibility.
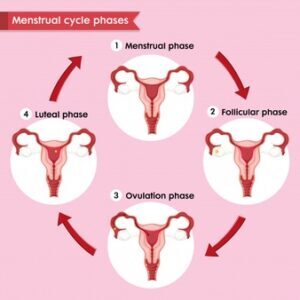
Phases of Ovulation
During the menstrual cycle, a period of elevated hormones describes the ovulation process. This process has the following three phases:
1. The follicular or periovulatory phase: A sheet or layer of cells present around the ovum begin to look more like mucus and expand. In this phase, the uterus lining starts to become thick. Ideally begins from day 1 of menses to Day 14 (for a typical 28-day cycle )
2. The ovulatory phase: A hole or stigma gets formed by the secreted enzymes; the ovum and its cell network then use the stigma to proceed into the fallopian tube; this is the fertility period and typically lasts from twenty-four to forty-eight hours. (usually between day 14 +/-3 days before and after)
3. The luteal or postovulatory phase: The LH gets secreted. The embryo gets implanted into the uterus or womb; the unfertilized egg stops secreting the hormones and dissolves within twenty-four hours (last 14 days of the cycle).
Also Read: How to avoid pregnancy naturally?
FAQs related to Ovulation
- When does Menstruation Occur?
On average, a woman’s menstrual cycle lasts between twenty-eight to thirty-two days. The beginning of each menstruation cycle gets considered as the first day of a woman’s menses. The egg is generally released twelve to sixteen days before the next period starts. Typically, most women begin to menstruate between ten to fifteen years of age; this is the same time when women begin to ovulate and have the ability to conceive. This period gets termed as menarche. Ovulation generally stops post-menopause, between the ages fifty to fifty-one years of age on an average, but is still occurrent in the period leading up to menopause. This period gets termed perimenopause.
- How does one Detect Ovulation- What are the symptoms of the ovulation period?
Following are some of the ovulation symptoms that a woman may experience:
• Body temperature may increase slightly. It happens due to the progesterone hormone release, which gets secreted when an egg is released. Women are typically most fertile for two to three days before the temperature rises to its maximum. One can use a basal thermometer to keep track of the body temperature. Such thermometers are available in most drug stores or also online.
• The cervical mucus grows in volume and turns thicker due to the estrogen levels which rise during Ovulation. The consistency of the cervical mucus resembles egg whites during a woman’s most fertile point. This is known as ovulation discharge and is nothing to worry about and is normal.
• Some women experience slight pain in their lower abdomen; this pain is called mittelschmerz pain. Such pains may last for a few minutes or a few hours.
• One may also experience some light spotting, and the vulva or vagina may even seem to be slightly swollen.
• Finally, several ovulation predictor kits can be bought from drug stores; these kits spot increased LH in the urine right before Ovulation.
Also Read: First Signs of Miscarriage in Early Pregnancy
- What is an Ovulation Calendar?
An Ovulation calendar helps a woman predict the time she will be most fertile. Some apps and websites assist in designing customized ovulation calendars for women; these apps or websites create the ovulation calendar by asking questions such as:
• When did your last menstrual cycle start?
• How long do your menstrual cycles usually last?
• What is the duration of the luteal phase, or duration between the day after Ovulation till the end of your cycle?
Note: It is recommended to record your menstrual information for entry into a calendar. Tracking your menstrual cycle can also help to identify any menstruation irregularities.
What are some common disorders related to Ovulation?
Some issues that can lead to difficulty in conceiving or infertility are:
• Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): In this condition, the ovaries are enlarged, often with small cysts in them.
• Hypothalamic dysfunction: This occurs when the production of the LH and FSH hormones is disturbed.
• Premature ovarian insufficiency: This is when the production of eggs stops prematurely because of the drop in estrogen levels.
• Excess prolactin or hyperprolactinemia: This condition occurs due to an anomaly in the pituitary gland, which generates hormones.
- Always remember to consult a doctor to know more about your Ovulation and menstrual cycle.
Quick Tips on Trying to Get Pregnant
• Avoid alcohol, caffeine, and smoking as this may prevent the egg from being fertilized and affect the quality of the female egg. Alcohol, caffeine, and smoking can affect Ovulation adversely.
• Exercise breathing control as it increases your chances of conceiving.
• Supplements like folic acid are formulated for conception as they help with the nutritional requirements for women trying to conceive.
• Less stress and reasonable hours of sleep (8 to 10 hrs)
Credits:
Dr.Sharanya.T M.S.OG ,
- Fellow in Reproductive Medicine (ICOG) Managing Director, Mint Hospitals
- ADYAR Director, BM Newlife and IVF center,
- Nanganallur: Medical Director at Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan
- Medical College, Perambalur ( 2012-2015)Fellow in Reproductive medicine( ICOG recognized )
- Embryology from Pearl Academy, MBBS, and MSOG from SRMC, Chennai
- Follow Now on: Bmhospitals.com , Minthospitals.com , FB- Sharanya Thiagarajan , Instagram – Smart Ovaries
Follow us-
Instagram/ Facebook/ Youtube/ Pinterest
Also Read:





Leave a Reply